Telogen Effluvium – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Telogen Effluvium, a phenomenon characterized by the thinning and shedding of hair from the scalp, was first identified by Kligman in 1961 as a disorder affecting the hair follicles. It manifests as a diffuse hair loss, typically following periods of significant bodily stress, and is often temporary in nature. Despite hair loss, the hair follicles remain intact, allowing for potential regrowth. It’s essential to grasp the natural hair growth cycle, which consists of three main phases: Anagen (growth phase), Catagen (transitional phase), and Telogen (falling phase). Telogen Effluvium specifically denotes the shedding of hair in the Telogen phase. This article elucidates the symptoms, causes, available treatments, and preventive measures for Telogen Effluvium.
Symptoms and Signs of Telogen Effluvium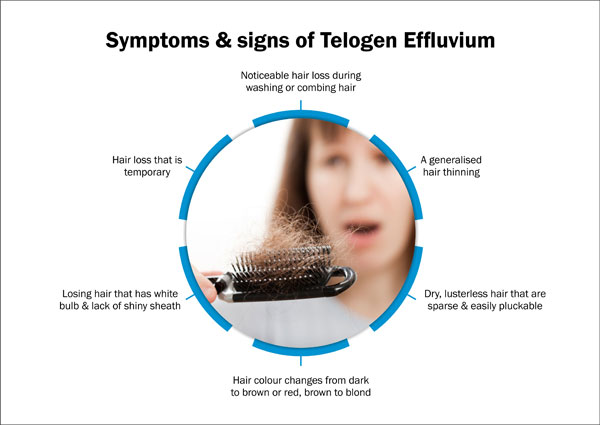
Telogen Effluvium presents various symptoms and signs, including:
-
- Increased shedding of hair, especially during washing or combing
- Maintenance of a healthy-looking scalp despite hair loss
- Generalized thinning of hair across the scalp
- Temporary nature of hair loss
- Shedding of hair with a white bulb and a lack of shiny sheath
- Dry, lackluster hair that is sparse and easily plucked
- Changes in hair color, such as darkening or lightening
Diagnosis of Telogen Effluvium
Medical History: A thorough medical history is crucial, particularly focusing on recent stressful events that may have triggered the hair loss. Additionally, observation of hair for the presence of a white bulb is essential for diagnosis.
Laboratory Testing: While laboratory testing is not always necessary, it may be conducted in certain cases to confirm the diagnosis. Some experts may analyze a hair sample to determine the Anagen to Telogen ratio of the hair growth cycle, providing a more accurate diagnosis. In cases of chronic Telogen Effluvium, medical tests such as thyroid tests, blood analysis, or enzyme analysis may be required to identify metabolic or biological causes.
Several laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis of Telogen Effluvium, including:
-
- Hair Pull Test: This test involves grasping a bunch of hair containing 40 to 60 hair strands and gently pulling. In Telogen Effluvium, more than 10% of the hair may be easily pulled out from the scalp.
- Hair Pluck Test (Trichogram): This test examines the hair to determine if more than 25% of hair is in the Telogen phase.
- Wash Test: The patient washes their hair after a specified period, and the lost hair is collected and counted to assess the extent of hair loss.
Understanding Hair Loss in Telogen Effluvium at NIS
How Hair Loss Occurs in Telogen Effluvium?
To comprehend the origin of Telogen Effluvium, it’s essential to grasp the hair growth cycle. A typical healthy hair undergoes three distinct phases: Anagen (growth phase), Catagen (transitional phase), and Telogen (falling phase).
-
- Anagen: This phase, lasting 2 to 3 years, involves cell division within the hair bulb, resulting in hair growth. At any given time, around 80 to 90% of hair remains in this stage.
- Catagen: Lasting approximately one month, this transitional phase marks the end of the growth phase. While the hair follicle shrinks, the hair remains intact. Only about 1% of hair follicles are in the catagen phase at any given time.
- Telogen: The final phase of the hair growth cycle, lasting about 3 months, is characterized by hair shedding. As hair enters the Telogen phase, it falls out from the scalp, after which the healthy hair follicle re-enters the Anagen phase to continue the growth cycle.
For healthy hair, the ideal Anagen to Telogen ratio (A/T ratio) is 80:20. However, various stressful events such as pregnancy, metabolic disorders, or injury can disrupt this balance, causing a significant number of Anagen hairs to stop growing prematurely and enter the Catagen phase, followed by the Telogen phase. This disruption leads to diffuse hair loss and a thinner appearance of the hair on the scalp.
Prevention of Telogen Effluvium
Since Telogen Effluvium can result from various factors like pregnancy, aging, or hormonal imbalances, maintaining healthy hair is crucial for prevention. Strategies for preventing Telogen Effluvium include:
-
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing stress effectively
- Ensuring adequate sleep
- Consulting a trichologist to switch medications that may cause hair loss
- Reducing consumption of unhealthy foods that increase bodily toxins
Treatment of Telogen Effluvium
While Telogen Effluvium often resolves on its own within 6 to 8 months, treatment focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause of stress, such as pregnancy or metabolic disorders. Treatment may include:
-
- Adjusting or discontinuing medications known to induce the Catagen phase
- Treating underlying metabolic or hormonal disorders
- Supplementing with iron, zinc, or proteins
- Consuming an iron-rich diet
- Applying minoxidil topically to promote hair growth
Prognosis of Telogen Effluvium
With the resolution of Telogen hair shedding and the emergence of new Anagen hair within 6 to 8 months, the prognosis for Telogen Effluvium is positive. Correcting underlying causes, reducing stress, and maintaining a healthy diet can further improve outcomes.
Causes of Telogen Effluvium
Telogen Effluvium can be triggered by various factors that disturb the hair growth cycle’s normal balance. Common causes include emotional stress, major surgery, pregnancy, illnesses, medications, or nutritional deficiencies.
Who Does Telogen Effluvium Affect?
Telogen Effluvium can affect individuals of any gender who have experienced emotional or physical stress. Women, however, may be more susceptible due to hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause. Chronic Telogen Effluvium is also more commonly reported in women.


